

Chlamydia trachomatis in relation to female infertility

14 January, 2019
According to data provided by the WHO (2019), there are more than one million cases of sexually transmitted diseases in the world every day, and the majority of these diseases are caused by eight pathogens. Syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis are curable while hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus, human immunodeficiency virus and papillomavirus are not.
The infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common sexually transmitted bacterial infection in the world. (Malhotra, M. et al., 2013).
What are the effects of this bacteria on women?
- Mucopurulent cervicitis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: between 20% and 30% of all cases are due to a Chlamydia infection. (Malhotra, M. et al., 2013)
- Infertility caused by tubal factors
- Gestational complications such as premature rupture of membranes, chorioamnionitis, preterm birth, or neonatal infections such as conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
- Chronic, recurrent or re-infections are the most dangerous situations. Recurrence is caused by the fact that Chlamydia remains in the spleen and lymph nodes. (Malhotra, M. et al., 2013).
In reproductive terms, one of the main causes of feminine sterility is the tubal factor. The most severe of these is hydro salpinx, which is intimately related to this bacterial infection.
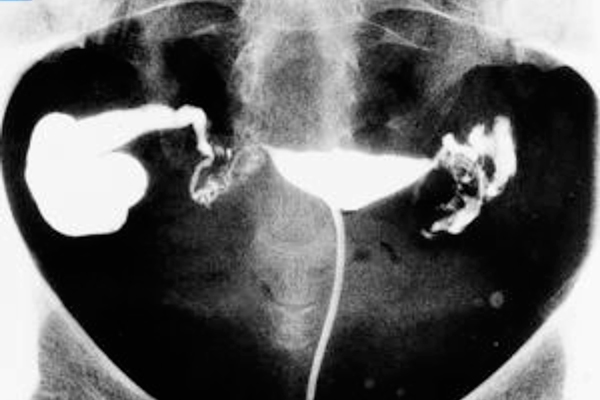
What is a hydro salpinx?
- This condition is defined as a distal obstruction of the fallopian tube with a dilation of its light and accumulation of fluid inside. It has been proven that hydro salpinx in in vitro fertilization cycles is associated with reducing pregnancy rates by one half, a significant decrease in implantation rates, and an increase in the rate of spontaneous abortions and ectopic pregnancies. (Strandell, A. et al., 1994).
What are the mechanisms that cause this negative effect on reproduction?
- Embryo toxic effect: the liquid in the hydro salpinx has a negative effect on embryonic development.
- Toxic effect on embryonic receptivity: the hydro salpinx liquid produces an alteration in the expression of certain substances related to the implantation process.
- Mechanical effect: the hydro salpinx liquid can pull the embryos along or simply position itself between the endometrium and the embryo, thus preventing their implantation.
- Increased uterine contraction: the pressure gradient caused by fluid accumulation may increase uterine contractibility.
How is this pathology diagnosed?
- Hysterosalpingography: this radiological technique is based on injecting a liquid contrast through the cervix in order to measure the tubal permeability by means of X-rays. It is very useful in the diagnosis of this particular pathology, as it can detect even a small hydro salpinx.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: An ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging method using a vaginal transducer. It only allows us to diagnose large caliber hydro salpinx or to diagnose it indirectly by observing the fluid in the endometrial cavity.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy: A surgical procedure that allows access to the inside of the abdomen and pelvis through a minimal incision from the navel. A camera allows us to visualize all the structures and to verify that the contrast is flowing through the tubes.
- Salpingoscopy: allows the tubal mucosa to be evaluated laparoscopically.
What is the treatment?
- Salpingectomy: resection and removal of the uterine tube. It is the treatment of choice for large hydro salpinx.
- Reconstructive surgery: used in mild cases where the tubal mucosa is not affected. However, it requires a highly specialized surgical team and increases the rate of ectopic pregnancy.
- Palliative surgery: indicated when the pelvis prevents correct access to the tube. It is based on the sealing of the tubes.
- Puncture and drainage: this is done with the guide of an ultrasound. It does not appear to have any positive effect on a reproductive level and may even increase the risk of complications.
- Antibiotic treatment: this is regularly prescribed due to the fact that it is related to the Chlamydia infection.

What is our role regarding this pathology?
It is true that the Chlamydia infection has an early detection rate due to the presence of abnormal vaginal secretions. Nevertheless, from 70% to 80% of women show no symptoms, which can bring about complications such as salpingitis, endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy and tubal factor-linked infertility, (Malhotra, M. et al., 2013). As professionals in assisted reproduction, we must know how to detect this pathology through a simple cytology and microbiological cultivation in addition to knowing how to treat the complications that clearly affect female sterility.
Would you like to know more about sexually transmitted diseases and their relationship to reproduction?
Official Master in Biotechnology of Assisted Human Reproduction
Personalized training
Related courses

Online
Online Course on Immunology and Hematology
Start: 02/12/2026
Online courses
Course fee:
250 €

Online
Online course: Fundamentals in Reproductive Genetics
Start: 02/12/2026
Online courses
Course fee:
150 €

Online
Assisted Reproduction Fundamentals
Start: 06/11/2026
Online courses
Course fee:
150 €

